Efforts toward decarbonization Decarbonization Initiatives

As a leader in decarbonization in thermal technology,
We promote the development of technologies and products to achieve carbon neutrality in 2050.
In recent years, governments around the world have set targets for significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions based on international frameworks, and companies are required to develop technologies and products with a focus on environmental measures that will contribute to the realization of these targets. In this context, we are accelerating our efforts to contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gases in industrial furnaces and related industries, which are estimated to account for approximately 17% of domestic CO₂ emissions.
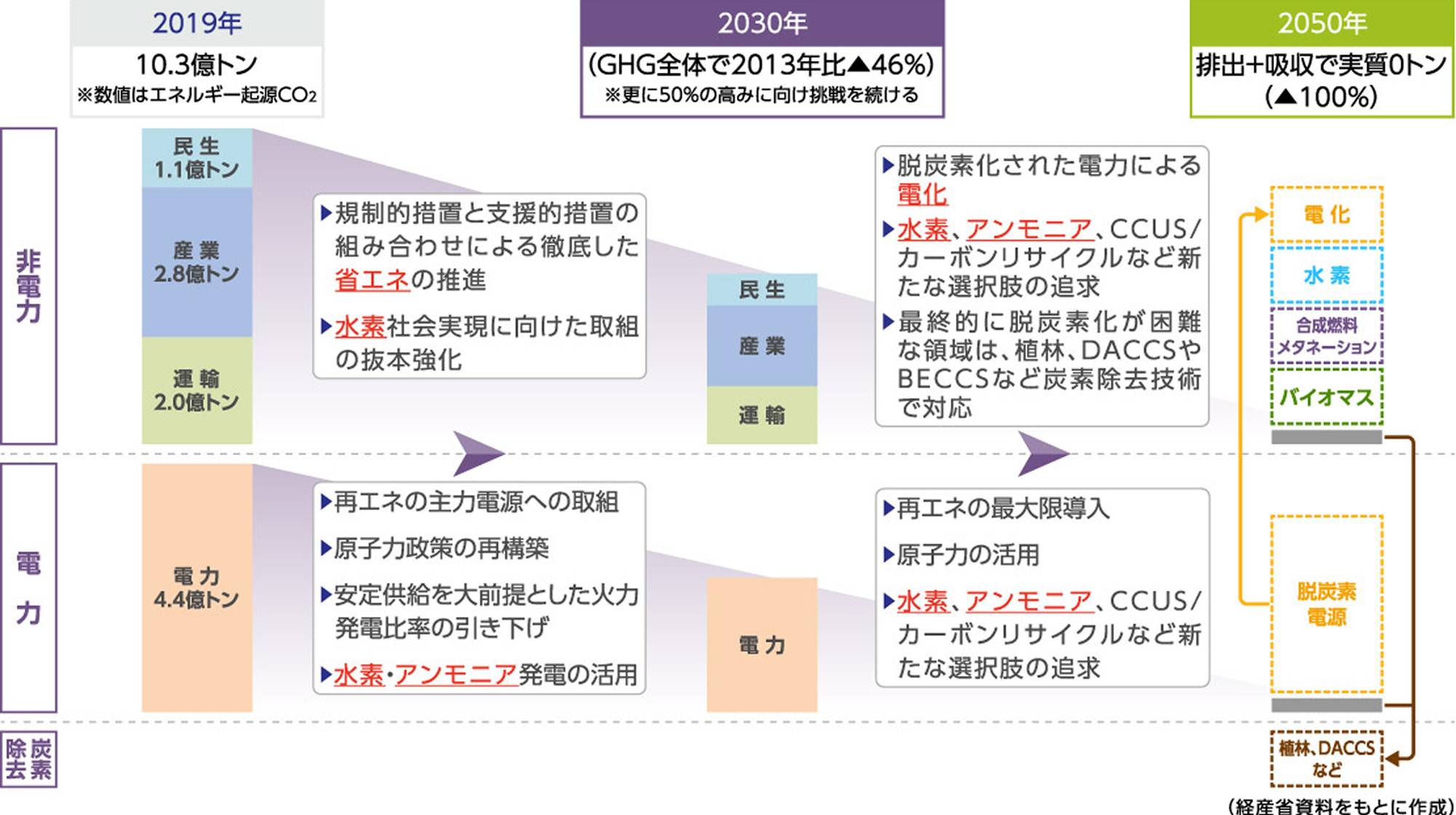
Image of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction
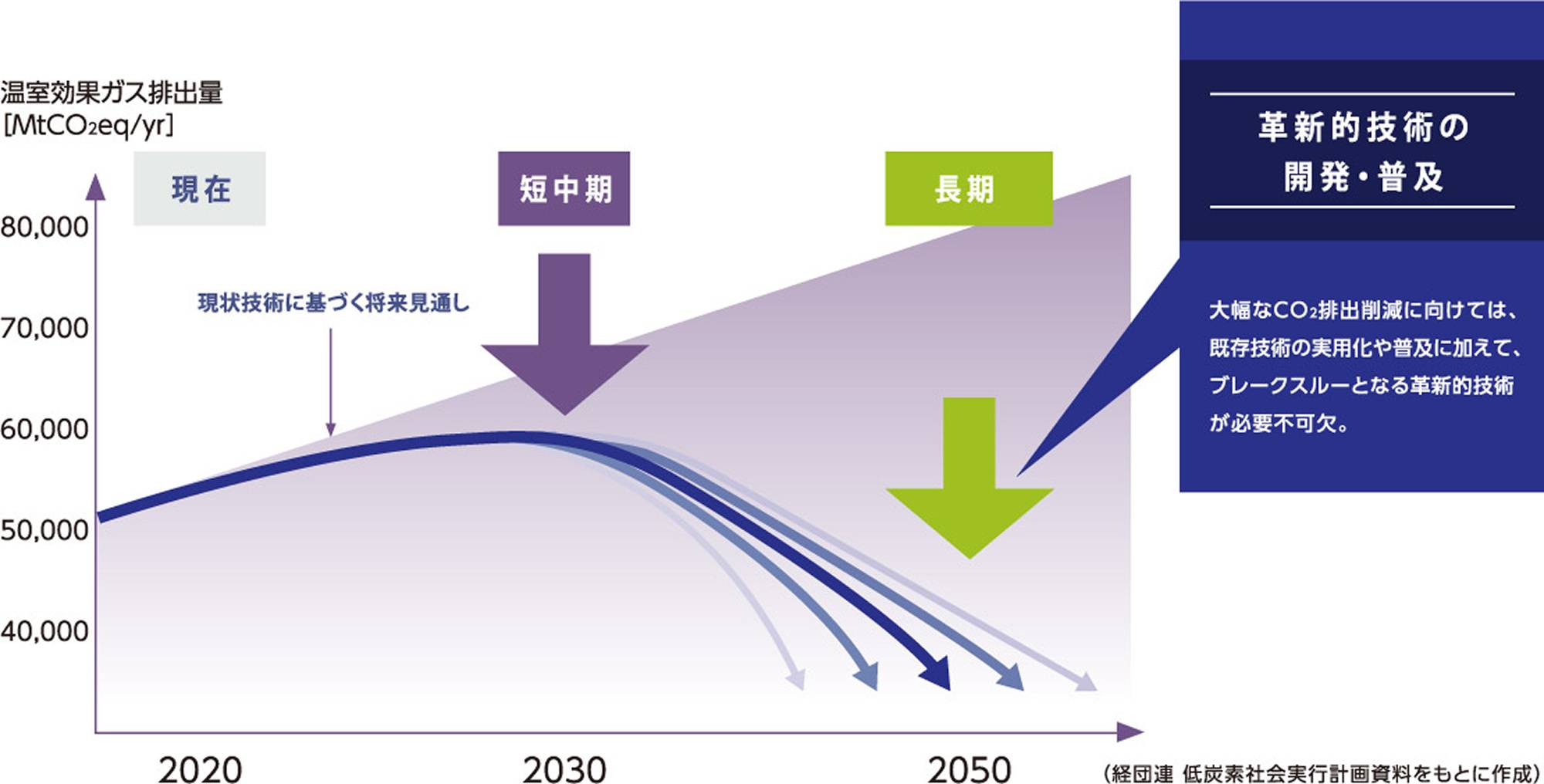
Image of Japan's transition to carbon neutrality in 2050

Our Response Topics

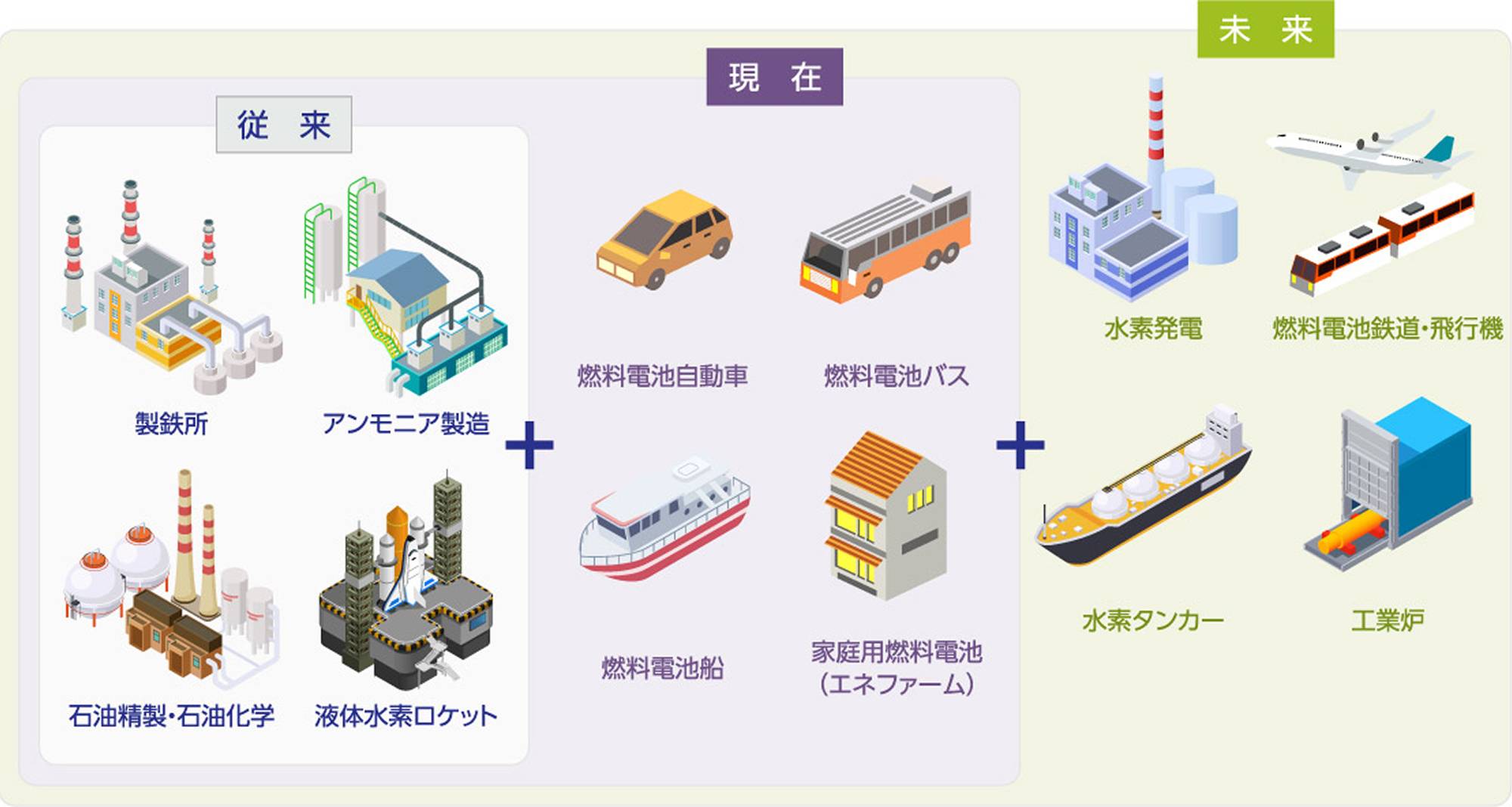
Hydrogen in decarbonization
Hydrogen has been mainly used in the industrial sector, such as in steel mills, but in recent years it has attracted attention for its advantages such as "no CO₂ emissions when used," "two types of energy can be supplied (electricity and heat)," "can be used in emergencies," and "can be made from local resources," and is used as a clean energy source to fuel vehicles such as cars and buses, and in EneFarm, which simultaneously produces electricity and heat in the home. It is expected to be used as an alternative to fossil fuels and as a means of energy storage in a variety of situations in the future.
Technologies we work on
- Hydrogen Burner
- Radiant tube hydrogen burner
- Hydrogen-fired superheated steam technology ( Contract testing here from )

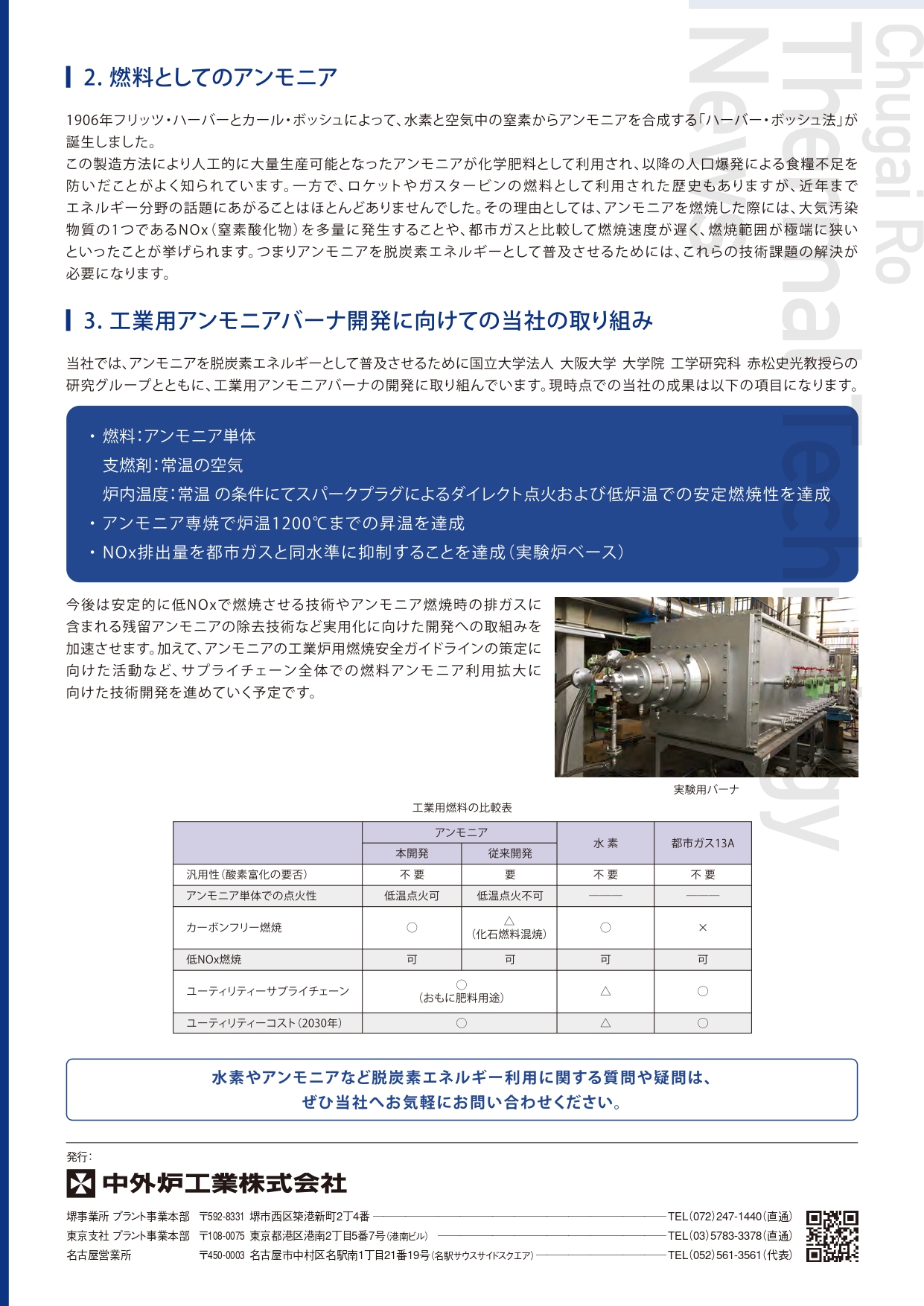
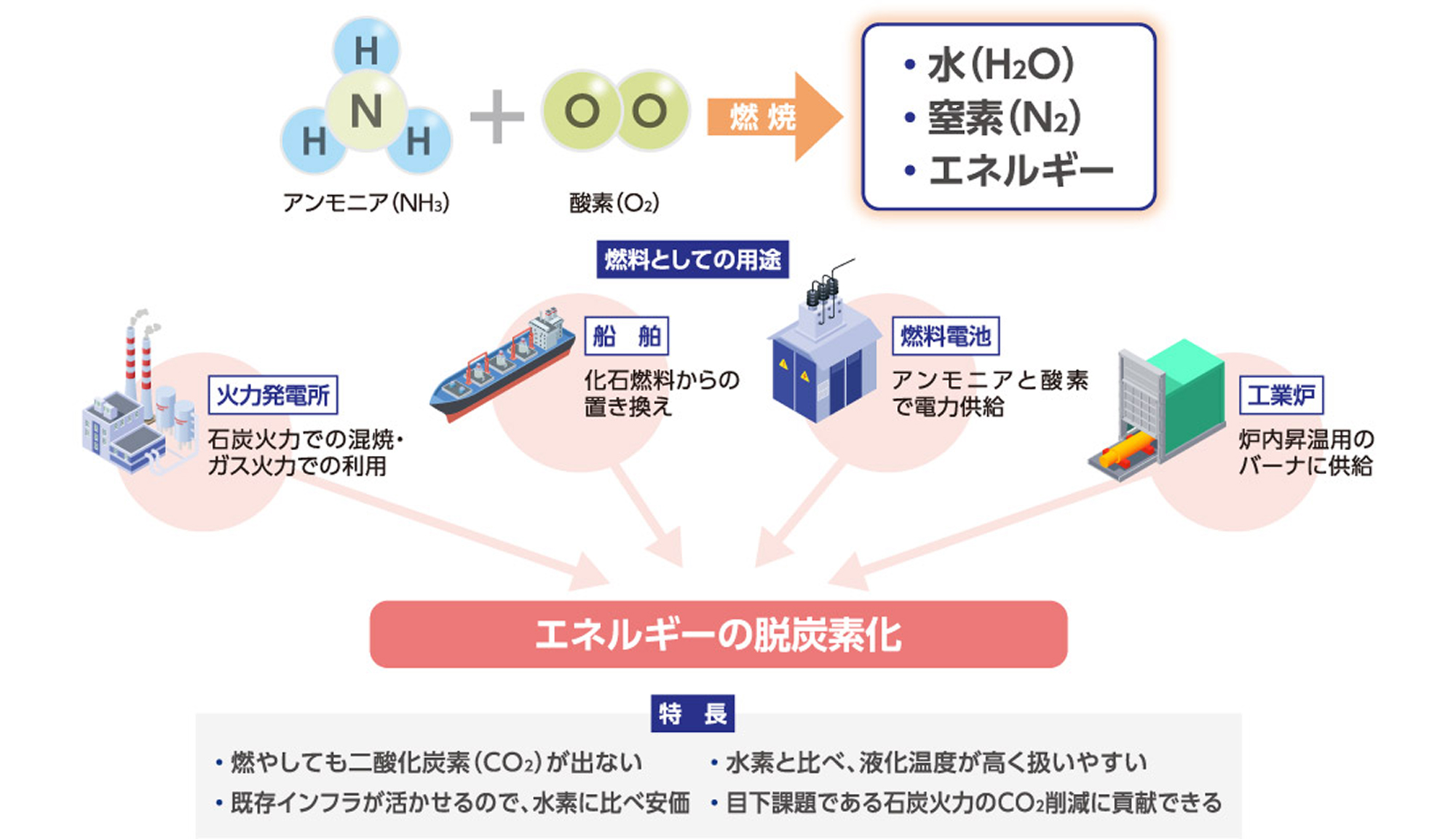
Ammonia in decarbonization
Ammonia, a compound of hydrogen and nitrogen, is used as a raw material for chemical fertilizers, etc. Like hydrogen, it does not emit CO₂ when burned, and although it is less flammable than hydrogen, it is easy to liquefy and handle. It is therefore considered more practical than hydrogen, and is attracting attention as a new trump card for decarbonization.
Ammonia, a promising next-generation fuel

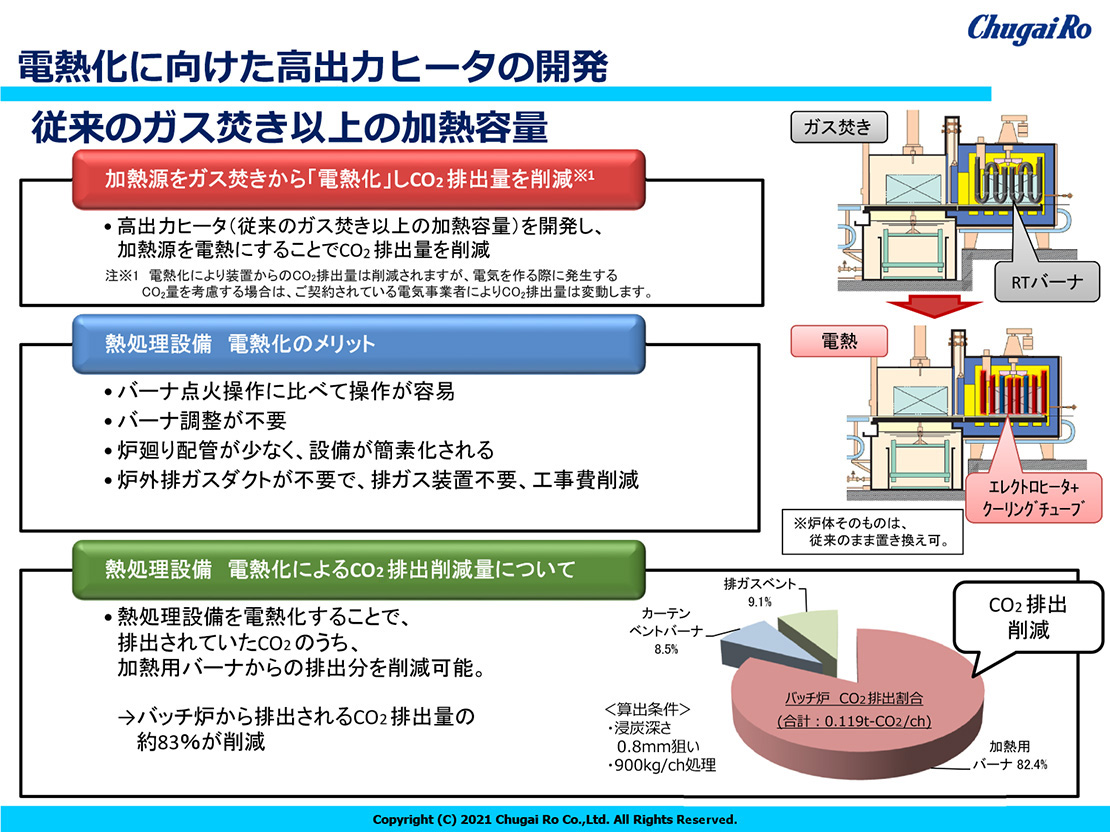
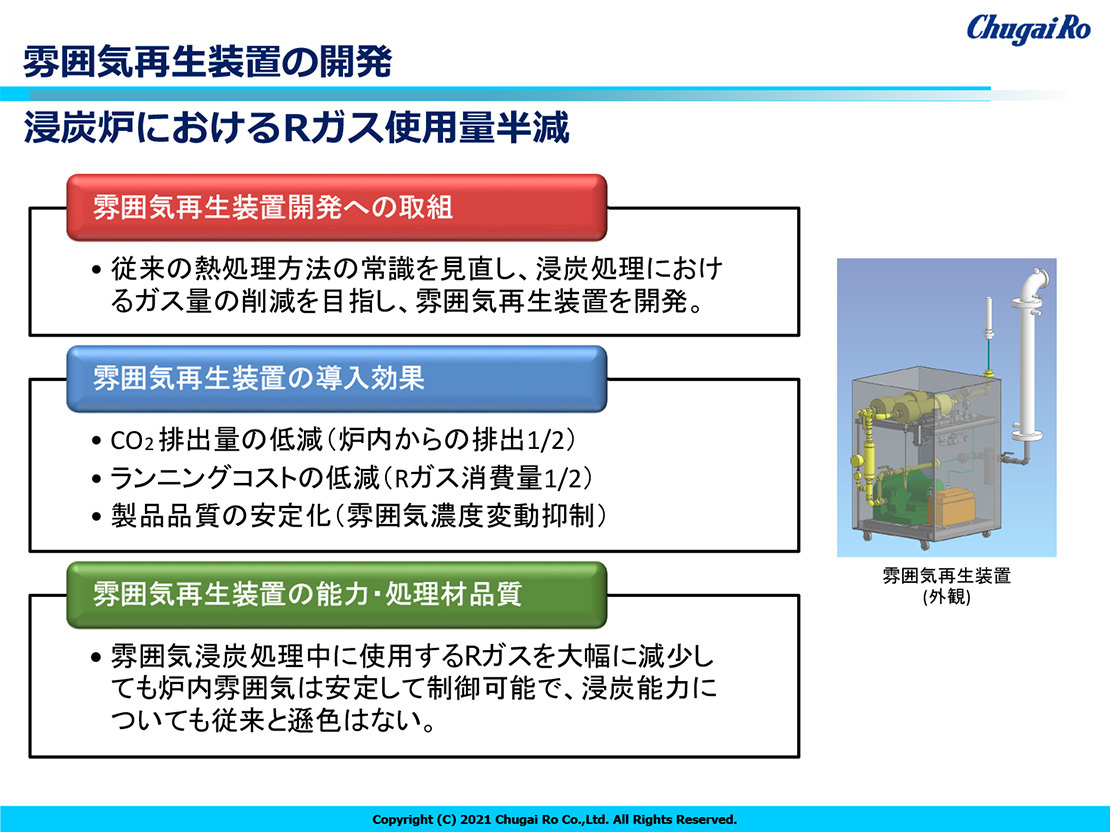
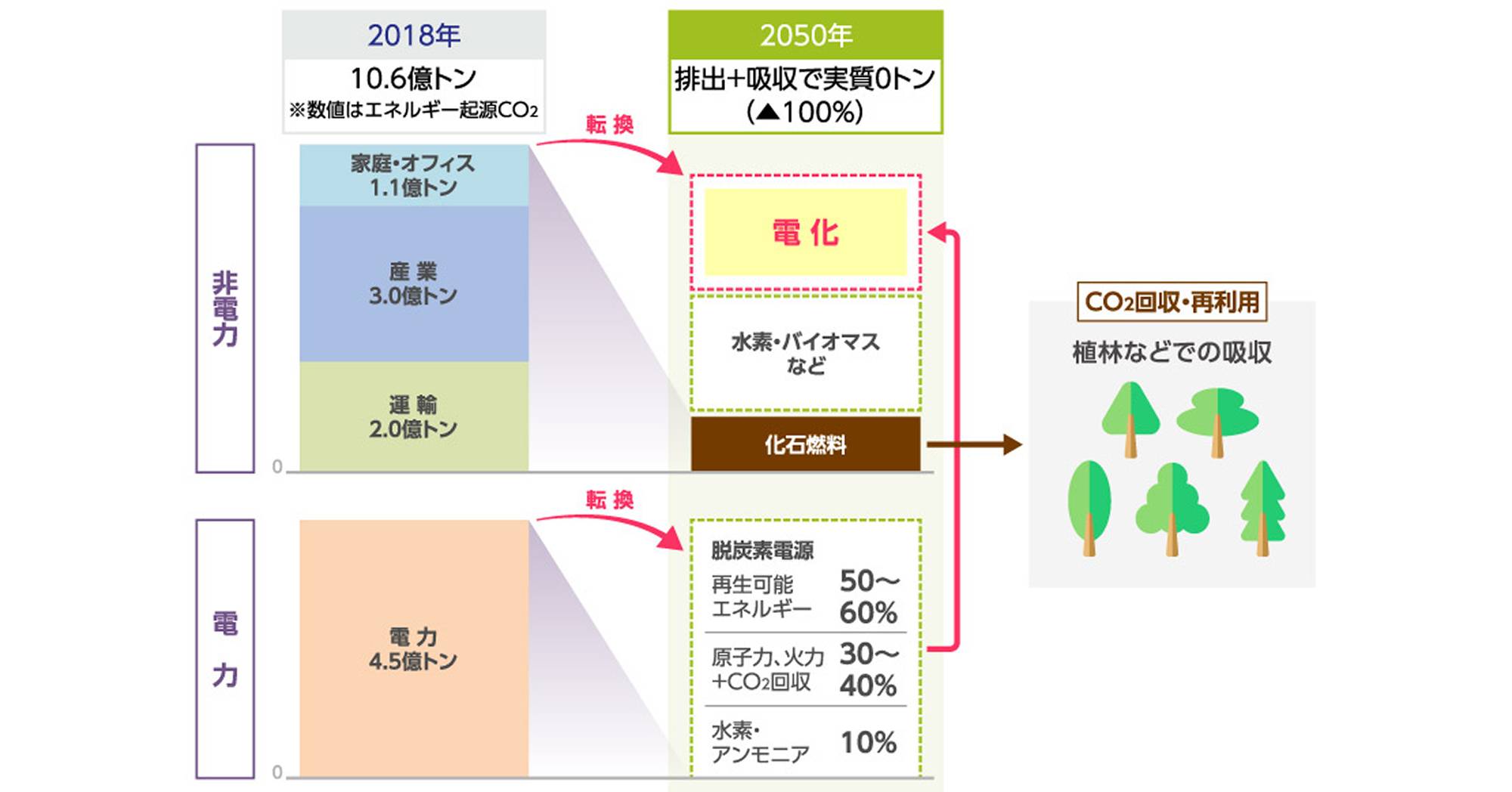
Electrification in decarbonization
Electrification, which replaces fossil fuels such as oil, coal, and gas, which emitCO2, with electricity as the energy source for daily life and economic activities, is an indispensable item for achieving carbon neutrality. emissions during power generation in the electric power sector and to use that power as much as possible through the spread of "electrification".
Image of the shift to electrification for domestic decarbonization
Technologies we work on

Further new ideas to develop unique decarbonization technologies
As a leading company in thermal technology, which is expected to play an active role in decarbonization, Chugai Furnace Manufacturing will continue to propose technologies and products to meet new needs.
Technologies we work on
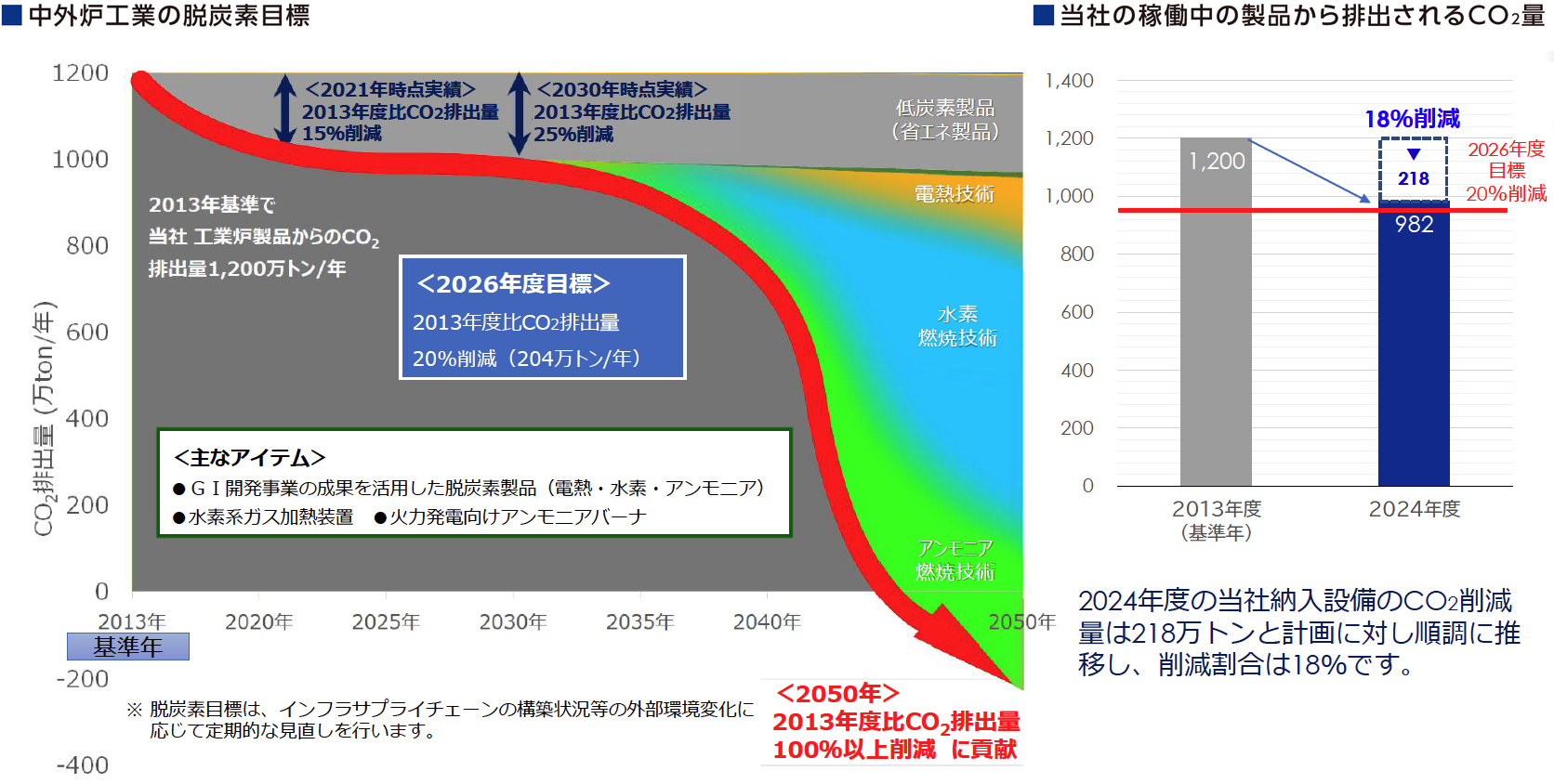
Chugai Ro's Decarbonization Goals
Since the "use of our products" portion of our supply chain emissions is particularly large, we have decided to set a decarbonization target for 2050 based on our standards. The vertical axis of the graph shows the amount of CO₂ emitted from our products in operation. As of 2013, the base year of the Paris Agreement target for Japan, this amount was approximately 12 million tons of CO₂, or roughly 1% of Japan's total emissions. The goal has been set to reduce this amount to virtually zero by 2050.
Since it is impossible to actually reduce emissions to zero, we intend to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, including CO₂ reductions in products other than our existing products.
<Most recent situation
As an indicator of this medium-term plan, we aim to reduce CO₂ emissions by 20% of the fiscal 2013 level by fiscal 2026, the final year of the plan.
In FY2024, the amount of CO₂ emissions reduction at facilities delivered by MCC was 2.18 million tons, well within the plan, and the reduction ratio was 18%.
(Reference) Our CO₂ emissions in Scope 1 and 2
Please refer to the following table for the results for FY2021 to FY2024.
| fiscal year (usu. April 1 to March 31) | Fiscal Year 2021 | Fiscal Year 2022 | Fiscal Year 2023 | Fiscal Year 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope 1 | 496 | 596 | 547 | 660 | |
| Scope 2 | market standard | 1,248 | 1,037 | 1,147 | 1,446 |
| Location Criteria | 1,480 | 1,472 | 1,367 | 1,524 | |
*Scope 1: CO₂ emissions directly emitted by the company. City gas was calculated based on the then current version of the "List of Emission Factors by Gas Supplier. Diesel oil and gasoline were calculated based on the then-current version of the "Emission Unit Database for Calculation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Organizations through Supply Chains" by the Ministry of the Environment and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. Kerosene was calculated based on the Ministry of the Environment's "List of Calculation Methods and Emission Factors for Calculation, Reporting, and Publication Systems. Propane and butane were calculated based on the "Guidelines for CO₂ emissions intensity of propane, butane, and LP gas" by the Japan LP Gas Association.
*Scope 2: Indirect CO₂ emissions from the use of energy purchased from other companies (in our case, electricity). Calculated based on the then-current version of the "List of Emission Factors by Electric Utility" by the Ministry of the Environment and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.
For companies that need help with environmental considerations and site improvements
CHUGAI RO CO., LTD. is a group of engineers with a wide variety of know-how and experience.
We are promoting a shift to decarbonization-ready industrial furnaces and burners on a global scale to achieve carbon neutrality.
Please consult with us for IT implementation and energy conservation promotion for on-site issue resolution as well as social issue resolution.