Hydrogen-Oxygen Combustion Superheated Steam Technology
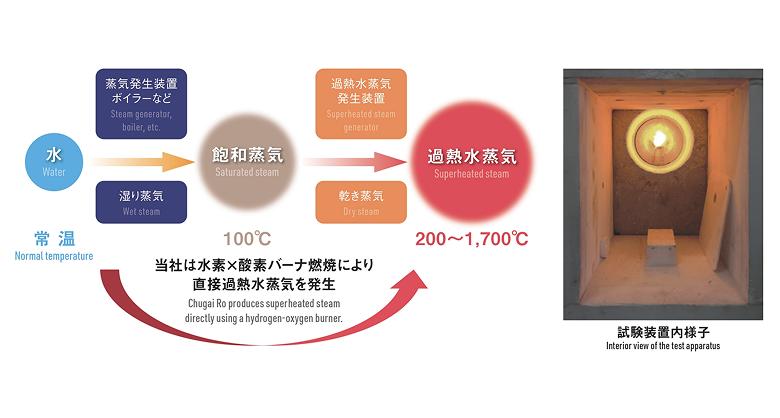
By harnessing high-temperature superheated steam produced through hydrogen and oxygen combustion, this new heating technology achieves zero CO₂ emissions.
What is superheated steam?
Superheated steam is a colorless, transparent steam gas that is produced by continuing to heat saturated steam after it has evaporated at 100°C.
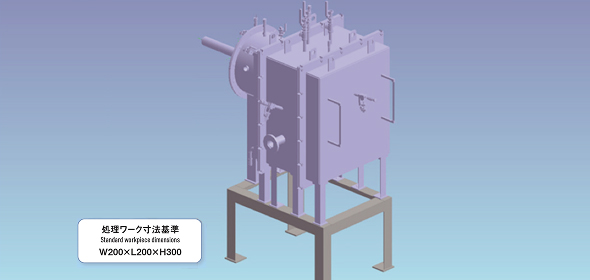
Equipment Features
- 1. Superheated steam is generated through the combustion of hydrogen and oxygen (no heater required).
- 2. The process produces superheated steam at 1,700°C.
- 3. Flames with zero CO₂ emissions contribute to industrial evolution.
Features and advantages of Hydrogen-Oxygen Combustion Superheated Steam Technology
- 1. It enables processing at low to ultra-high temperatures ranging from 200 to 1,700°C.
・This achieves ultra-high-temperature processing that exceeds the capabilities of electric superheated steam generators. - 2. The high heat transfer performance enables quick, uniform heating.
・At lower temperatures, the material is rapidly heated by the latent heat of the condensation released when superheated steam changes to water, whereas at higher temperatures, heating is achieved through the high radiative heat transfer of steam. - 3. Steam-driven carbon gasification reaction at temperatures above 800°C
・In a superheated steam atmosphere exceeding 800°C, carbon released
from the treated material undergoes a steam gasification reaction*, enabling the decomposition of organic solvents, resins, and similar substances without self-ignition, even in an oxidizing environment.
( *Steam gasification reaction: A chemical reaction in which carbon reacts with steam at temperatures of around 800–1,000°C, splitting into carbon monoxide and hydrogen as a result. ) - 4. It enables heating in both oxidizing and non-oxidizing atmospheres.
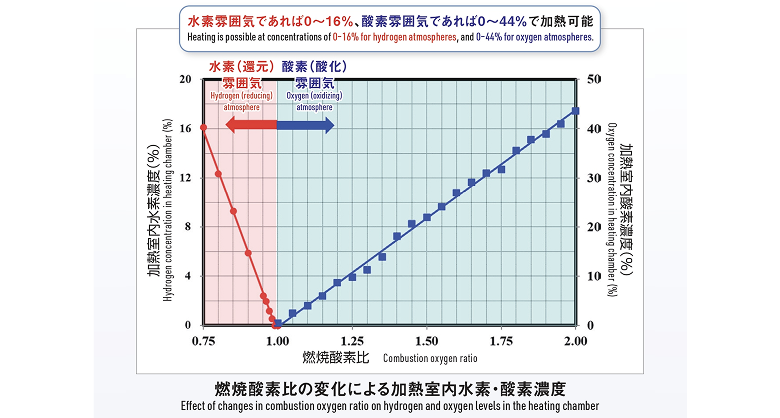
・By adjusting the hydrogen-oxygen ratio, the atmosphere inside the furnace can be switched from oxidizing to non-oxidizing and vice versa.
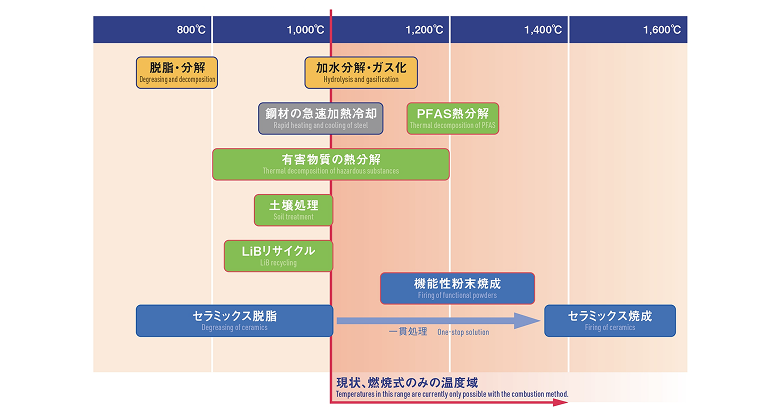
Example Applications
Superheated steam offers a wide range of benefits depending on the treated material.
An example of superheated steam put to effective use
・Thermal treatment of spent lithium-ion batteries from vehicles

Organic solvents in the electrolyte and resin in separators pose a risk of thermal runaway due to reactions with oxygen at high temperatures. However, they can be safely decomposed through the steam gasification reaction of superheated steam, which prevents them from reacting with oxygen.
Chugai Ro is equipped with hydrogen-oxygen combustion superheated steam testing systems and
provides testing support for those adopting equipment.
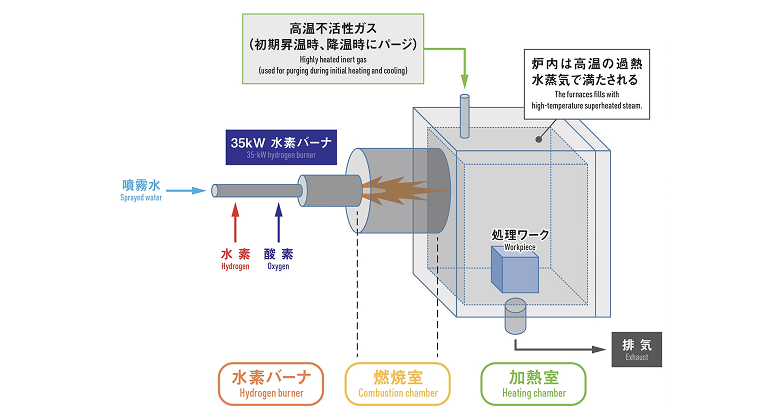
Hydrogen-oxygen combustion superheated steam testing systems
- These systems consist of a hydrogen burner, a combustion chamber, and a heating chamber.
- Superheated steam produced using the hydrogen burner heats the material to be treated in the heating chamber.
- By spraying water into the center of the burner, the furnace temperature and the amount of superheated steam produced can be adjusted.
- The atmosphere inside the furnace can be switched from oxidizing to non-oxidizing and vice versa by adjusting the hydrogen-oxygen ratio.
What Hydrogen-Oxygen Combustion Flame Looks Like
The amount of superheated steam can be adjusted by introducing sprayed water in addition to the exhaust gas from hydrogen combustion.